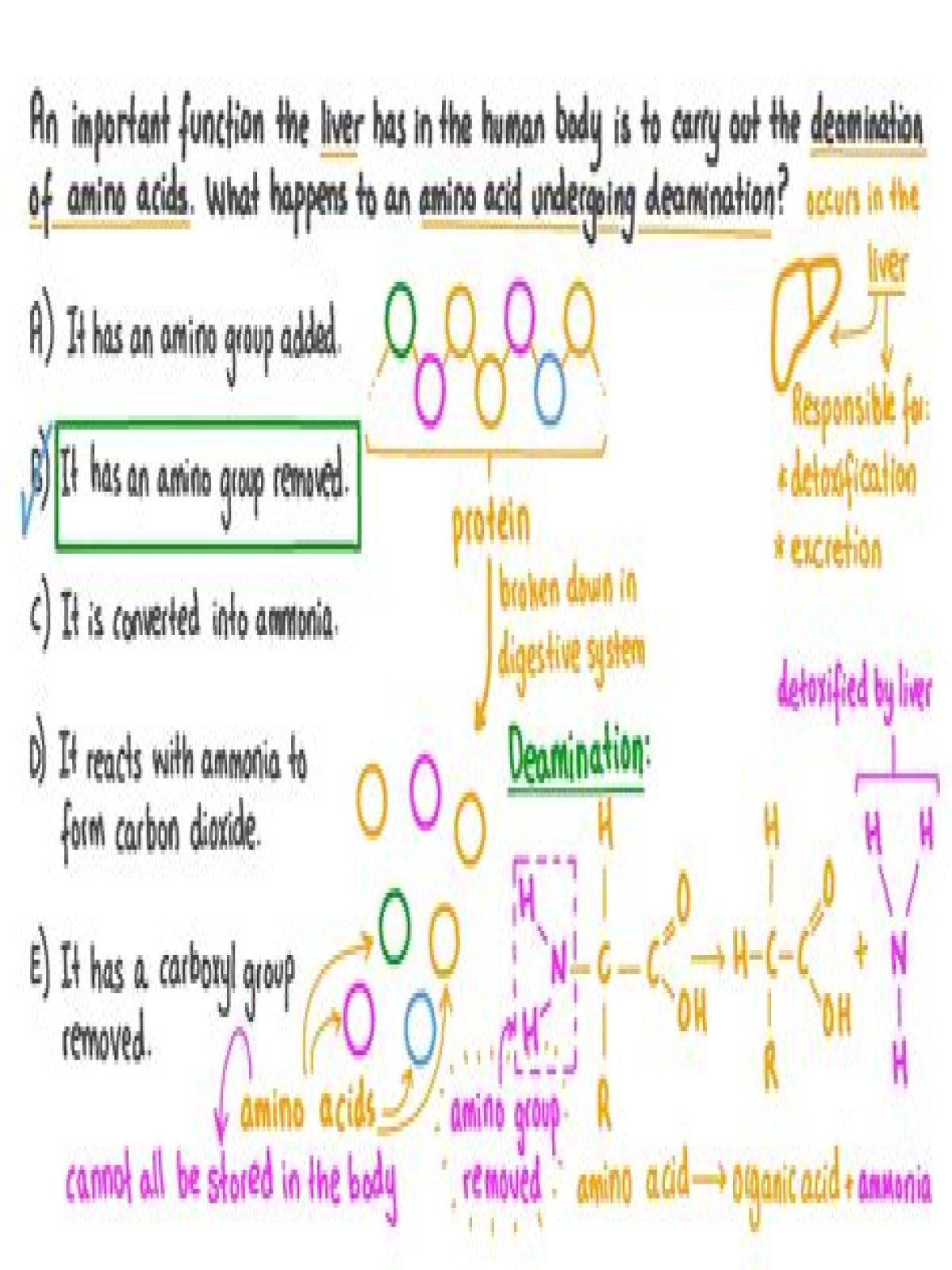
What is the deamination process
Typically in humans, deamination occurs when an excess in protein is consumed, resulting in the removal of an amine group, which is then converted into ammonia and expelled via urination. This deamination process allows the body to convert excess amino acids into usable by-products.
- Does deamination remove nitrogen?
- What are the 4 stages of the nitrogen cycle?
- What is deamination answer?
- What is deamination quizlet?
- What is transamination and oxidative deamination?
- Is deamination anabolic or catabolic?
- What is oxidative deamination give example?
- What is deamination waste product?
- What is deamination in biology class 9?
- What happens to cytosine on deamination?
- What is nitrification in nitrogen cycle?
- What is the correct pathway for nitrification?
- What is the difference between nitrogen fixation and nitrification?
- In which test does Deamination occur?
- Is deamination a catabolic?
- What is deamination and decarboxylation?
- Does deamination produce ATP?
- What is the nitrogen containing product of an oxidative deamination reaction?
- What species is formed from the transamination and oxidative deamination of the amino group in an amino acid?
- Which of the following is a product in oxidative deamination of glutamate?
- What is liver deamination?
- What is deamination GCSE?
- Which product is obtained after deamination of aspartate?
- Is deamination an oxidation?
- What is non oxidative deamination?
- Where does transamination and deamination occur?
- What is an alpha Ketoacid?
- Who is in nitrogen balance?
- Does deamination produce glucose?
Does deamination remove nitrogen?
In the liver, nitrogen destined for disposal is removed from amino acids in a two-step process referred to as “trans-deamination”.
What are the 4 stages of the nitrogen cycle?
- Nitrogen Fixation.
- Ammonification/ Decay.
- Nitrification.
- De-nitrification.
What is deamination answer?
Deamination is the removal of an amine group from a molecule. An enzyme that is responsible for this reaction is called deaminases.What is deamination quizlet?
What is deamination? The enzymatic removal of an amine group (NH2) from an amino acid. … Amino acids connected by peptide bonds to form a polypeptide or protein.
What is transamination and oxidative deamination?
Oxidative Deamination In the breakdown of amino acids for energy, the final acceptor of the α-amino group is α-ketoglutarate, forming glutamate. … The amino group can then be passed on through transamination reactions, to produce other amino acids from the appropriate α-keto acids.
Is deamination anabolic or catabolic?
Catabolic Processes The main processes of catabolism include the citric acid cycle, glycolysis, oxidative deamination, the breakdown of muscle tissue and the breakdown of fat.
What is oxidative deamination give example?
oxidative deamination A reaction involved in the catabolism of amino acids that assists their excretion from the body. An example of an oxidative deamination is the conversion of glutamate to α-ketoglutarate, a reaction catalysed by the enzyme glutamate dehydrogenase. See deamination.What is deamination waste product?
Urea Is Produced During Deamination and Is Eliminated as a Waste Product. The ammonia released during deamination is removed from the blood almost entirely by conversion into urea in the liver.
What is deamination of a write types of deamination?Deamination is the process by which an amino group will be removed from the molecule. … Ammonia is highly toxic to the human system, and the enzymes will convert it into urea or uric acid by adding carbon dioxide molecules in the urea cycle. This process also occurs in the liver.
Article first time published onWhat is deamination in biology class 9?
Complete answer:The deamination is the process by which the amino acids are broken down if there is an excess of protein intake. The amino group is removed from the amino acid and converted to ammonia. Ammonia is toxic to the human system and the enzymes convert it to urea or to uric acid molecules in the liver.
What happens to cytosine on deamination?
Spontaneous deamination converts cytosine to uracil, which is excised from DNA by the enzyme uracil-DNA glycosylase, leading to error-free repair. … These studies provide direct evidence that the deamination of cytosine is a significant source of spontaneous mutations.
What is nitrification in nitrogen cycle?
Nitrification. Nitrification is the process that converts ammonia to nitrite and then to nitrate and is another important step in the global nitrogen cycle. Most nitrification occurs aerobically and is carried out exclusively by prokaryotes.
What is the correct pathway for nitrification?
Nitrification is a two-step process in which NH3/ NH4+ is converted to NO3-. First, the soil bacteria Nitrosomonas and Nitrococcus convert NH3 to NO2-, and then another soil bacterium, Nitrobacter, oxidizes NO2- to NO3-. These bacteria gain energy through these conversions, both of which require oxygen to occur.
What is the difference between nitrogen fixation and nitrification?
The key difference between nitrogen fixation and nitrification is that the nitrogen fixation is the process of converting atmospheric nitrogen into ammonium ions while the nitrification is the process of converting ammonium ions into nitrite or nitrate ions.
In which test does Deamination occur?
Phenylalanine deaminase test also known as phenylpyruvic acid (PPA) test is used to test the ability of an organism to produce enzyme deaminase. This enzyme removes the amine group from the amino acid phenylalanine and produces phenylpyruvic acid (PPA) and ammonia i.e. oxidative deamination of phenylalanine.
Is deamination a catabolic?
Removal of the α-amino group is the first step in catabolism of amino acids. It may be accomplished oxidatively or nonoxidatively.
What is deamination and decarboxylation?
The direct deamination and decarboxylation are two attractive strategies for the conversion of amino acids into respectively a,w-bifunctional carboxylic acids, and amines and amides.
Does deamination produce ATP?
Deamination results in net ATP formation except when serine and threonine deaminases are used, but there is the energy cost of synthesizing glutamine in extra-hepatic tissues.
What is the nitrogen containing product of an oxidative deamination reaction?
Oxidative deamination requires an amino transferase and a dehydrogenase. Ammonium ion (NH4 +) is liberated. NH4 + is a product of the breakdown of amino acids. NH4 + is required by cells for synthesis of nitrogen containing compounds.
What species is formed from the transamination and oxidative deamination of the amino group in an amino acid?
The amino acid is transaminated to produce a molecule of glutamate. Glutamate is the one amino acid that undergoes oxidative deamination to liberate free ammonia for the synthesis of urea. Once free ammonia is formed in peripheral tissues, it must be transferred to the liver for the conversation to urea.
Which of the following is a product in oxidative deamination of glutamate?
The glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) pathway and the Krebs cycle function. As shown here, oxidative deamination of glutamate by hGDH1 and hGDH2 generates α-ketoglutarate, ammonia and NADH or NADPH. While α-ketoglutarate is metabolized by the Krebs cycle, NADPH can be used for biosynthetic reactions.
What is liver deamination?
In the human body, deamination takes place in the liver. It is the process by which amino acids are broken down. The amino group is removed from the amino acid and converted to ammonia. The rest of the amino acid is made up of mostly carbon and hydrogen, and is recycled or oxidized for energy.
What is deamination GCSE?
The liver is involved in the process of deamination. This is the removal of the nitrogen-containing part of amino acids, to form urea, followed by the release of energy from the remainder of the amino acid.
Which product is obtained after deamination of aspartate?
1.1) catalyzes the reversible deamination of aspartate to produce fumarate and ammonia.
Is deamination an oxidation?
Oxidative Deamination. Introduction: Deamination is also an oxidative reaction that occurs under aerobic conditions in all tissues but especially the liver.
What is non oxidative deamination?
Nonoxidative deamination is a type of deamination reaction in which the removal of the amine group occurs without proceeding through an oxidation reaction. However, this type of deamination reactions liberates ammonia, producing the corresponding α-keto acids. … Histidase catalyzes this reaction.
Where does transamination and deamination occur?
Also, transamination occurs in all cell of the body while deamination occurs in the liver.
What is an alpha Ketoacid?
Alpha-keto acids are the deaminated form of amino acids, which have been used in several applications in the medicine, food, and feed industries. In vivo, alpha-keto acids are ketogenic or glucogenic precursors, which regulate protein turnover.
Who is in nitrogen balance?
Nitrogen balance: Healthy adults usually maintain constant lean body mass and neither accumulate protein nor lose protein mass. Since their combined nitrogen intake (mainly as protein) more or less equals their nitrogen losses, they are said to be in nitrogen balance.
Does deamination produce glucose?
When deaminated, amino acids can enter the pathways of glucose metabolism as pyruvate, acetyl CoA, or several components of the citric acid cycle. For example, deaminated asparagine and aspartate are converted into oxaloacetate and enter glucose catabolism in the citric acid cycle.