What is an SQL deadlock?
Considering this, what causes a SQL deadlock?
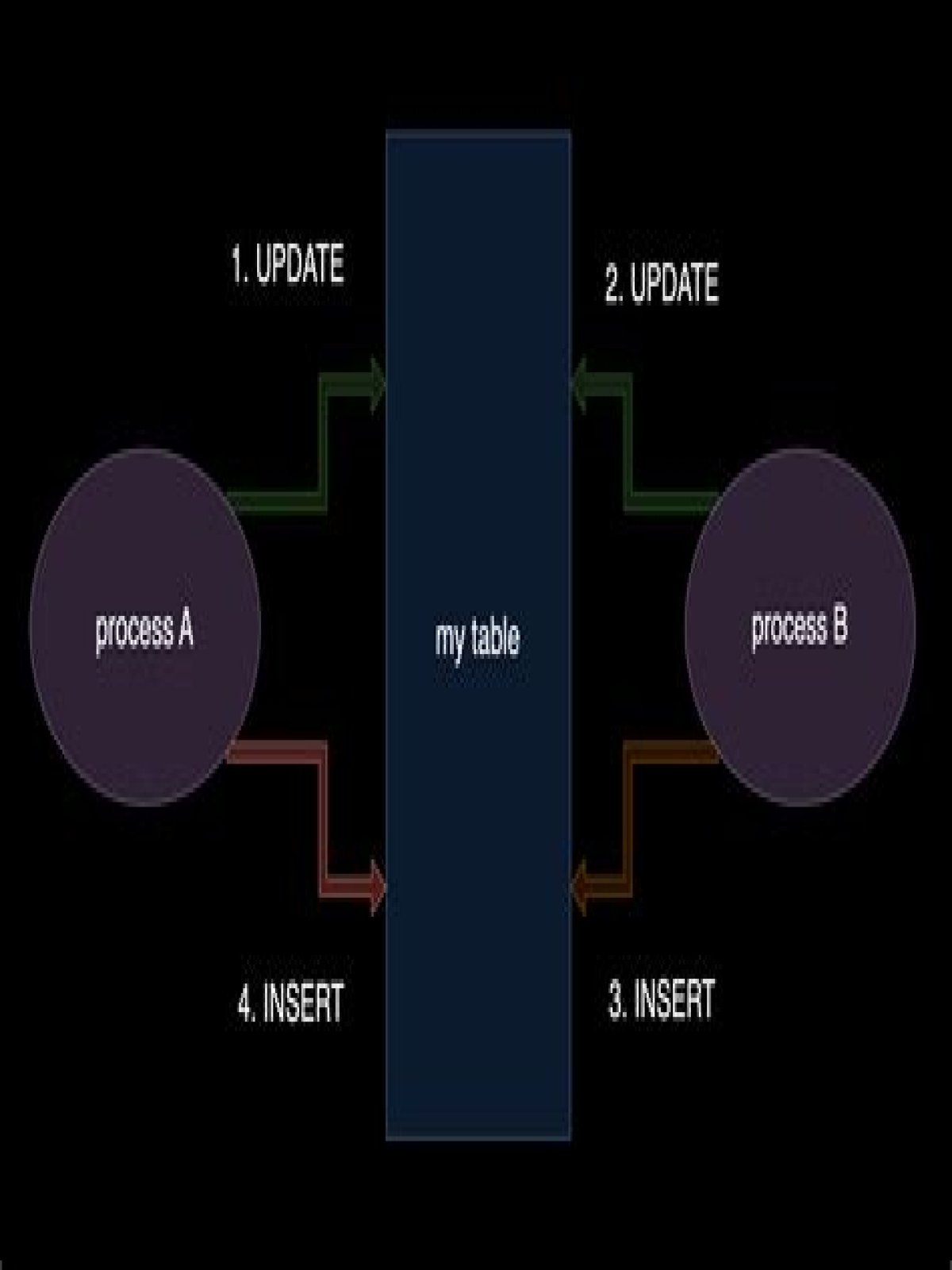
The Cause of Every Deadlock in SQL Server A deadlock happens when two (or more) transactions block each other by holding locks on resources that each of the transactions also need. For example: Transaction 1 holds a lock on Table A. This is a cyclical dependency and results in what is called a deadlock.
Also, what is deadlock in SQL Server and how do we resolve? To resolve a deadlock, SQL Server has to rollback the cheapest of the 2 transactions. In the context of SQL Server, the cheapest transaction is the transaction that has written the fewer bytes to the transaction log. SQL Server implements the deadlock detection in a background process called the Deadlock Monitor.
Keeping this in view, what is a deadlock in a database?
In a database, a deadlock is a situation in which two or more transactions are waiting for one another to give up locks. For example, Transaction A might hold a lock on some rows in the Accounts table and needs to update some rows in the Orders table to finish.
How can avoid deadlock in SQL Server?
Access objects in the same order.
- Access objects in the same order.
- Avoid user interaction in transactions.
- Keep transactions short and in one batch.
- Use a lower isolation level.
- Use a row versioning-based isolation level.
How do you avoid SQL deadlock?
What are the 4 conditions required for deadlock to occur?
- mutual exclusion. The resources involved must be unshareable; otherwise, the processes would not be prevented from using the resource when necessary.
- hold and wait or partial allocation.
- no pre-emption.
- resource waiting or circular wait.
How can deadlocks be resolved?
- Dampen your adversarial urge. First and foremost, dampen any adversarial urge.
- Shared problem solving. View any conflict as an opportunity to problem solve.
- Don't Counter-propose… Reframe.
- Build on their ideas.
- Appeal to their senses; don't beat them up.
How do you simulate a deadlock?
- Launch the SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
- Open a query window.
- Begin a transaction using BEGIN TRAN.
- Below the begin transaction, wright an update query against a record in a table, say PurchaseOrders.
- Execute the statement along with the begin transaction.
- Now, open another query window.
What causes a deadlock?
How can deadlock be resolved?
How can deadlock be prevented?
What is deadlock and its prevention?
What is deadlock and its types?
What is deadlock example?
What are the three basic techniques to control deadlocks?
- Deadlock preventation . A transaction requesting a new lock is aborted when there is the possibility that a deadlock can occur.
- Deadlock detection. The DBMS periodically tests the database for deadlocks.
- Deadlock avoidance.
What is a deadlock error?
What is two phase locking in DBMS?
What is rollback in DBMS?
What is false deadlock in DBMS?
How do you check if there is a deadlock in SQL Server?
- Using SP_LOCK, you can find the WAIT status for blocking sessions:
- Using sys.sysprocesses:
- Using common DMV:
- Using sys.dm_tran_locks:
- Enable required trace flags to log DeadLock related information in Tracefile:
- Count total number of DeadLock: